Fire Extinguisher Training: Who Should Use Them and When
August 12, 2025
Fire Extinguisher Cylinder Care: Preventing Damage and Leaks
August 18, 2025Fire extinguishers are critical safety tools that could mean the difference between a small incident and a devastating disaster. Whether you have one at home, in your car, or in the workplace, knowing how a fire extinguisher works and how to use it correctly is crucial. Most importantly, understanding the science behind these devices helps you pick the right one and act confidently in emergencies.
In this blog, we’ll explore the three main mechanisms fire extinguishers use to stop fires, cooling, smothering, and chemical interruption, and guide you on choosing, using, and maintaining these life-saving tools.
The Basics of Fire and the Fire Triangle
Fire is a chemical reaction that needs three key elements to keep burning:
- Heat: The source of ignition and energy
- Oxygen: Supports combustion from the air
- Fuel: Anything that can burn, like wood, paper, or gasoline
Together, these form the classic fire triangle. In reality, we talk about the fire tetrahedron, which adds the chemical chain reaction that sustains the fire after it starts.
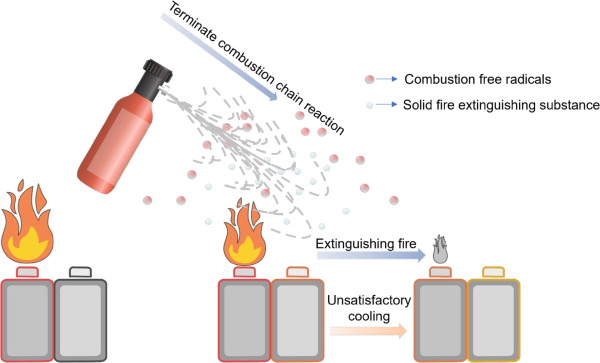
When a fire extinguisher operates, it targets one or more elements of this tetrahedron to stop combustion, by removing heat, oxygen, fuel, or interrupting the chemical reaction.
Fire Extinguishers and Their Core Mechanisms
1. Cooling
Cooling is the most intuitive way to fight a fire: lower the temperature to prevent combustion. Water extinguishers are the most common cooling type, effective on Class A fires such as those that involve wood, fabric, paper, and other ordinary combustibles.
When sprayed, water absorbs the heat creating vapor and cooling the fuel source below its ignition temperature.
Example: In a home fire caused by burning sofa cushions or paper, a water extinguisher quickly lowers the temperature and stops the flames.
Limitations: Water is dangerous for oil (grease) fires and electrical fires because it can spread fire or cause electric shocks. For these, use other types like foam or CO₂ extinguishers.
2. Smothering
Smothering works by starving the fire of oxygen, which is one of the critical components of fire. Foam, CO₂ gas, and fire blankets use this principle effectively.
- Foam extinguishers cover the burning liquid to form a thick blanket that prevents oxygen from reaching the fuel. These are ideal for Class B fires, such as gasoline spills.
- The CO₂ fire extinguisher releases carbon dioxide gas which displaces oxygen, suffocating the fire without leaving any messy residue behind. This makes CO₂ extinguishers perfect for electrical fires (Class C) and offices with sensitive electronic equipment.
Additional Example: Many vehicles are equipped with car fire extinguishers that often use dry chemical or CO₂ to quickly eliminate fires involving the engine or fuel lines without damaging electronics.
3. Chemical Interruption
Chemical interruption is a more advanced method where extinguishing agents interfere with the fire’s chemical chain reaction. Dry chemical powders like monoammonium phosphate or sodium bicarbonate are commonly used.
These dry chemicals coat the fuel, separating it from oxygen and breaking the fire’s self-sustaining chemical reaction. This makes them versatile, able to fight Class A, B, and C fires.
When is this method preferred? Dry chemical extinguishers are widely used in industrial, commercial, and residential settings because of their effectiveness across various fire types. They are also handy for kitchen fires involving flammable liquids or electrical faults.
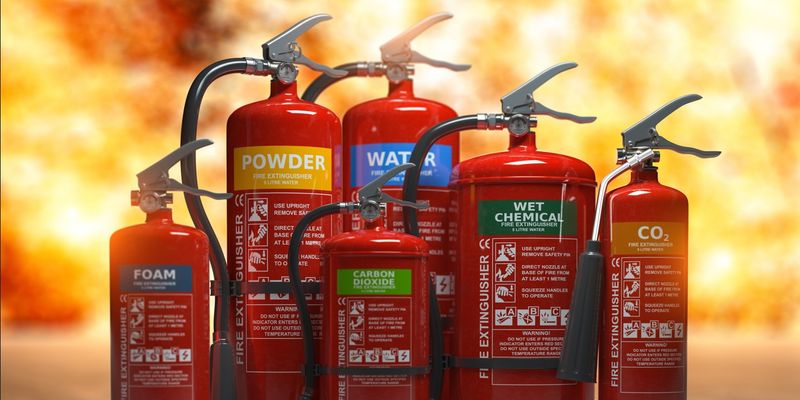
Types of Fire Extinguishers and Their Uses
Understanding fire classes helps you choose the right extinguisher:
- Class A: Ordinary combustibles like wood, paper, and cloth.
- Class B: Flammable liquids such as petrol, oil, paints.
- Class C: Electrical fires involving live electrical equipment.
- Class D: Fires involving combustible metals, rare but dangerous (magnesium, sodium).
- Class K: Kitchen fires involving cooking oils and fats.
Common fire extinguisher types:
| Fire Class | Extinguisher Type | Typical Uses |
| A | Water, Foam, Wet Chemical | Home fires, furniture, paper |
| B | Foam, CO₂, Dry Chemical | Petrol stations, paint shops |
| C | CO₂, Dry Chemical | Electrical workshops, offices |
| D | Dry Powder (special metals) | Metal factories |
| K | Wet Chemical | Commercial kitchens |
Fire Extinguisher Ball: A modern safety device gaining popularity, the fire ball automatically activates on detecting flame or heat and spreads extinguishing powder over the fire. This hands-free approach is especially useful in areas where immediate response is critical. In Pakistan, the fire extinguisher ball price is affordable, making it a practical choice for homes and offices alike.
Choosing the Right Fire Extinguisher
When selecting a fire extinguisher, think about:
- Where it will be used: Kitchens need wet chemical extinguishers for grease fires, whereas garages benefit from dry chemical or foam extinguishers.
- Type of possible fire hazards: In an office, a CO₂ fire extinguisher helps protect both electrical equipment and people.
- Size and ease of use: A large fire extinguisher cylinder can be cumbersome in small spaces, so a compact extinguisher or fire extinguisher ball might be better.
- Budget: Fire extinguisher price varies by type, quality, and capacity. It’s wise to invest in trusted brands that meet safety standards.
How to Use a Fire Extinguisher Effectively: The PASS Method
In an emergency, use the PASS technique to make your efforts effective and safe:
- Pull the safety pin to unlock the extinguisher.
- Aim the nozzle or hose at the base of the fire, not the flames.
- Squeeze the handle to release the extinguishing agent.
- Sweep from side to side, covering the entire fire base until it’s extinguished.
Safety tip: Always keep your back to an exit and keep a safe distance from the fire. If the fire grows or the room fills with smoke, evacuate immediately.
Maintenance and Safety Checks
Regular maintenance ensures your extinguisher works when you need it:
- Check the pressure gauge monthly and confirm it’s in the safe (green) zone.
- Inspect the fire extinguisher cylinder for dents, rust, or corrosion.
- Verify that safety seals and pins are intact.
- Ensure the extinguisher is visible and easily accessible.
- Replace or service extinguishers after use or once expired. Dry chemical and gas agents can weaken over time.
In Pakistan, it’s common practice to get local fire safety experts to service extinguishers and offer instructions on proper upkeep.
Additional Safety Tools: Fire Blankets and Fire Buckets
While fire extinguishers are essential, other tools add valuable support:
- Fire blankets can quickly smother small fires or help wrap around a person whose clothes are on fire.
- Fire buckets, often filled with sand or water, provide simple but effective fire-fighting means, especially in rural areas or workshops where more sophisticated equipment isn’t available.
Conclusion
Fire extinguishers save lives by working through three key mechanisms: cooling to reduce heat, smothering to cut oxygen, and chemical interruption to stop fire reactions. Each type caters to specific fire classes and hazards, so selecting the right one is essential to safety.
Remember, having a fire extinguisher is just the first step, knowing how it works, how to use it properly, and maintaining it regularly are equally important. Equip your home, car, and workplace with reliable fire safety gear.
For affordable, high-quality fire safety products including the latest fire extinguisher balls, CO₂ fire extinguishers, wet chemical fire extinguishers, and durable fire extinguisher cylinders, Haseen Habib offers trusted solutions tailored to your needs.
If you want personalized guidance on which fire extinguisher suits your needs or want to know the fire extinguisher price in Pakistan, reach out to Haseen Habib for expert advice and prompt service.